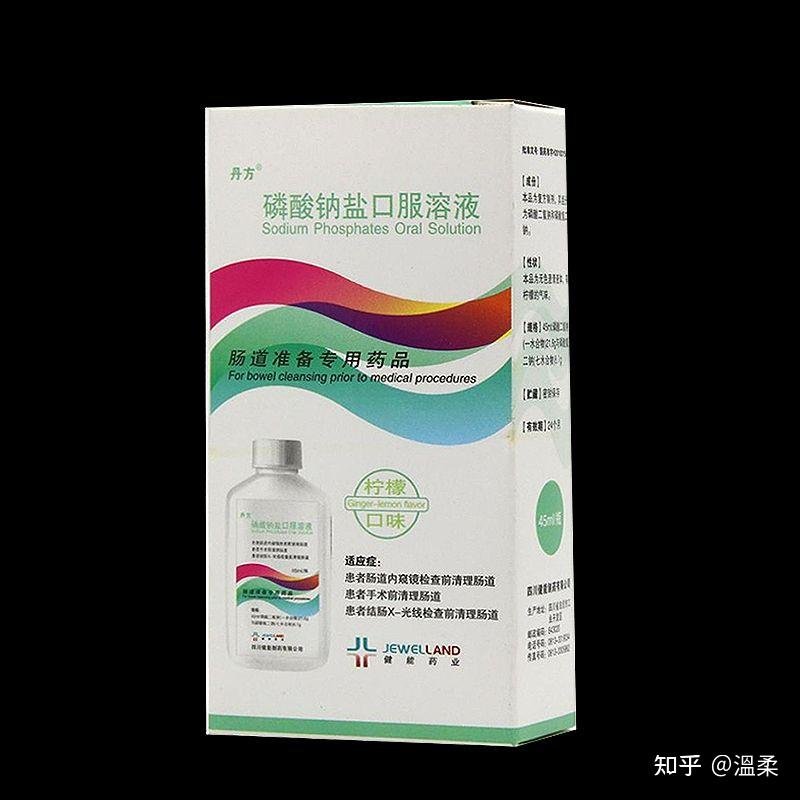
Sodium Phosphates Oral Solution
Effects and efficacy:
Sodium phosphate oral solution is a compound preparation, which consists of sodium dihydrogen phosphate and disodium hydrogen phosphate. It is an efficient and safe hyperosmotic laxative. It is mainly used to clean the intestines before patients’ colon X-rays and intestinal endoscopy or before surgery.
Usage and dosage:
Sodium phosphate oral solution is generally taken twice for intestinal preparation, 45ml each time. The first dose is at 7 pm the day before the operation or examination. The usage adopts a dilution scheme and is taken after dilution with more than 750ml of warm or cold water. The second dose is at 7 am on the day of the operation or examination (or at least 3 hours before the operation or examination), or as prescribed by the doctor, and the usage is the same as the first time. In order to obtain a good intestinal preparation effect, it is recommended that patients drink more water within their tolerance.
Adverse reactions:
Through observations in pre-market clinical trials, the most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) of taking sodium phosphate preparations or this product are abdominal distension, nausea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Transient electrolyte disorders (high/low sodium phosphate salts, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, and dehydration), fatigue, dizziness, allergic reactions, elevated liver function tests ALT and AST, and anal irritation symptoms may also occur during and after medication. Occasionally, drooling occurs. Allergic reactions (rash, purpura, edema, and lip paresthesia, etc.), acute phosphate nephropathy, renal failure, convulsions, and arrhythmias have also been found in post-marketing reports. Acute sodium phosphate nephropathy and renal impairment Taking this product may cause rare but serious acute sodium phosphate nephropathy and renal impairment. It has been reported that patients who use sodium phosphate preparations to clean the intestines before endoscopic examinations and before surgery may develop renal damage and acute sodium phosphate nephropathy (i.e., renal calcitonin deposition), which may lead to transient or permanent renal impairment (renal failure). Some patients require dialysis and/or transplantation. Most of the above adverse reactions occur in patients taking antihypertensive drugs (such as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor inhibitors) or diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is recommended that high-risk patients with renal impairment, who are receiving treatments that may cause a decrease in renal tubular filtration rate or may cause dehydration (such as diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor inhibitors, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), should use this product with caution. Such patients should replenish water before making laxative preparations and appropriate treatments. Convulsions It has been reported that patients with no previous history of convulsions may experience rare paroxysmal spasms and loss of consciousness after using sodium phosphate salts. Convulsions are related to electrolyte disorders and plasma hypoosmolarity. Arrhythmias It has been reported that patients may experience severe and rare arrhythmias and some QT interval prolongation after using sodium phosphate salts. QT interval prolongation is related to electrolyte disorders (such as hypokalemia and hyponatremia). It is recommended that this product be used with caution in patients at high risk of arrhythmias, such as those with a history of cardiomyopathy and difficult-to-control arrhythmias, QT interval prolongation, and recent myocardial infarction. It is recommended that such patients be closely monitored by electrocardiogram before and after medication.
Drug contraindications:
This product is contraindicated if you are allergic to it
Share:
Products
Our offers
Health Classification
Let us work together to protect precious health