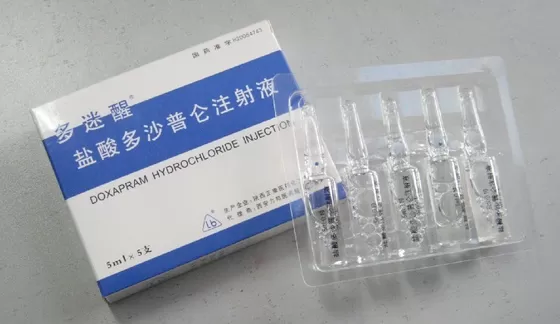
Doxapram Hydrochloride Injection.
Dosage and Administration:
Doxapram Hydrochloride Injection: 1. Intravenous injection: 0.5-1.0 mg/kg per body weight, not exceeding 1.5 mg/kg. If repeated administration is required, at least 5 minutes interval is required. The dosage per hour should not exceed 0.3 g (3 vials). 2. Intravenous drip: 0.5-1.0 mg/kg per body weight. Dilute with glucose and sodium chloride injection before use and drip intravenously until full effect is achieved. The total amount should not exceed 3 g (30 vials) per day. Doxapram Hydrochloride for Injection: 1. Intravenous injection: 0.5-1.0 mg/kg per body weight, not exceeding 1.5 mg/kg. If repeated administration is required, at least 5 minutes interval is required. The dosage per hour should not exceed 300 mg. 2. Intravenous drip: 0.5-1.0 mg/kg per body weight, diluted to 1 mg/ml with 5% glucose or 0.9% sodium chloride injection, the drip rate is determined according to clinical needs, 5 mg/minute at the beginning of intravenous drip, and can be reduced to 1-3 mg/minute after the effect is achieved. The total amount should not exceed 3g per day until the therapeutic effect is achieved.
Adverse reactions:
1. The blood system may cause a decrease in hemoglobin, hematocrit or red blood cell count, and too fast an infusion rate may cause hemolysis. There are also reports of patients with leukocytopenia experiencing leukocytopenia after taking the drug. 2. The cardiovascular system may cause increased blood pressure, and may also cause flat T waves, arrhythmias, chest pain, sphenoid artery or chest tightness. There are individual reports of atrioventricular block. 3. The central nervous system may cause irritability, nervousness, and convulsions. Other central adverse reactions include facial flushing, vomiting, paresthesia, fear, disorientation, headache, mydriasis, dizziness, extreme excitement, involuntary movements, muscle spasms, tendon hyperreflexia, myoclonus, positive bilateral Babinski sign, etc. 4. Endocrine metabolism may cause hyperglycemia and diabetes. 5. The gastrointestinal tract may cause abdominal distension, gastric retention, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Long-term nasogastric tube administration for the treatment of premature infants with apnea may cause positive stool occult blood and necrotizing enterocolitis. 6. Elevated blood urea nitrogen and proteinuria have occurred in the urogenital system. There have also been reports of bladder irritation symptoms, urinary incontinence and urinary retention. Sometimes it can cause fever in the genitals and perineum. 7. There are individual reports of liver toxicity. 8. There are reports of respiratory system dyspnea, cough, shortness of breath, laryngeal spasm, bronchospasm, hiccups and recurrence of pulmonary hypoventilation. 9. The skin may cause skin flushing and itching. 10. The musculoskeletal system may cause tendon hyperreflexia, myoclonus or muscle spasm. There are reports of muscle tremors.
Contraindications:
1. People who are allergic to the ingredients of this product. 2. Patients with hyperthyroidism. 3. Patients with pheochromocytoma. 4. Patients with cerebrovascular disease, brain trauma, and cerebral edema. 5. People with epilepsy or convulsions. 6. Patients with severe hypertension or coronary heart disease. 7.
Share:
Products
Our offers
Health Classification
Let us work together to protect precious health