Diclofenac Sodium Injection
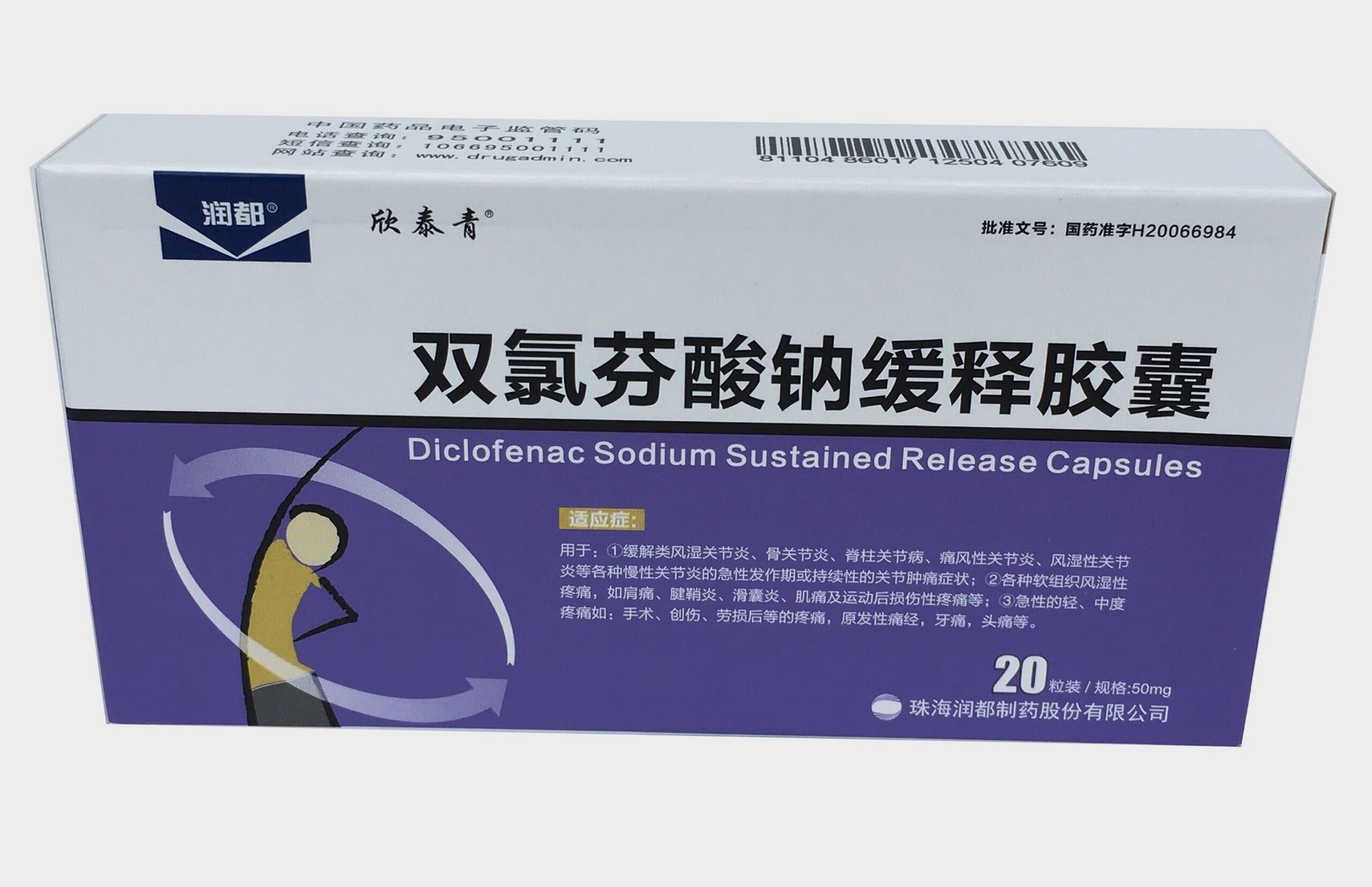
Functions and indications: Diclofenac sodium enteric-coated tablets: used for: (1) relieving joint swelling and pain symptoms of various arthritis such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, spondyloarthropathies, gouty arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.; (2) treating various non-articular soft tissue rheumatic pains, such as shoulder pain, tenosynovitis, bursitis, myalgia and pain after sports injuries, etc.; (3) acute mild and moderate pains such as post-surgery, post-traumatic, post-strain, dysmenorrhea, toothache, headache, etc.; (4) having an antipyretic effect on fever in adults and children. Diclofenac sodium double-release enteric-coated capsules: used for acute joint inflammation and gout attacks, chronic joint inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylosis and other inflammatory rheumatic diseases of the spine, pain related to degenerative diseases of the joints and spine, soft tissue rheumatism, swelling, pain or inflammation after trauma or surgery, treating dysmenorrhea and postoperative pain and inflammation caused by plastic surgery, dental surgery or other minor surgical procedures. It is also used to treat non-bacterial inflammation after ophthalmic surgery. Dosage and Administration: This product has a variety of dosage forms and specifications. The same medicine produced by different manufacturers may have inconsistent instructions. Please read the instructions carefully before taking the medicine and take the medicine according to the doctor’s instructions. Diclofenac Sodium Enteric-Coated Tablets: Oral. 1. As a regular dose, the initial daily dose is 100-150mg. For mild patients or patients who need long-term treatment, the daily dose is 75-100mg. The daily dose is usually taken in 2-3 times. 2. For primary dysmenorrhea, the daily dose is usually 50-150mg, taken in divided doses. The initial dose should be 50-150mg. If necessary, the dose can be increased to a maximum dose of 200mg/day within several menstrual cycles. Once symptoms appear, treatment should be started immediately and continued for several days. The treatment plan depends on the symptoms. 3. Common dosage for children: 0.5-2.0mg/kg per day, the maximum daily dose is 3.0mg/kg, taken in 3 times. Diclofenac sodium enteric-coated capsules: Oral, 50 mg (one capsule) at a time, twice a day, or as directed by a doctor. Diclofenac sodium suppositories: Take a plastic fingertip, put it on the index finger, take out the suppository, hold the lower end of the suppository, moisten it with a small amount of warm water, and gently insert it 2 cm into the anus. For adults, take 50 mg at a time, 50 mg-100 mg a day, or as directed by a doctor. Diclofenac sodium eye drops: Start taking the medicine on the first day after surgery, 4 times a day, 2 drops each time. Diclofenac sodium ointment: For external use. Depending on the size of the painful area, use 1-3 ml of this product, evenly apply it to the affected area, 2-4 times a day, and the total amount per day should not exceed 15 ml.
Adverse reactions:
Diclofenac sodium enteric-coated tablets: (1) Gastrointestinal reactions: The most common adverse reactions, seen in about 10% of patients, mainly stomach discomfort, burning sensation, acid reflux, poor appetite, nausea, etc., which can disappear after stopping the drug or symptomatic treatment. A few of them may have ulcers, bleeding, and perforation; (2) Neurological manifestations include headache, dizziness, drowsiness, excitement, etc.; (3) It causes adverse reactions such as edema, oliguria, and electrolyte imbalance. In mild cases, they can disappear after stopping the drug and receiving corresponding treatment; (4) Other rare reactions include transient increase in serum transaminase, and very rare jaundice, rash, arrhythmia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, etc., which can all recover after stopping the drug. Diclofenac sodium double-release enteric-coated capsules: The corresponding categories of adverse reactions of each drug are based on the following regulations: very common (>1/10); common (≥1/100 and <1/10); occasional (≥1/1000 and <1/100); rare (≥1/10000 and <1/1000); very rare (<1/10,000). The following are possible adverse reactions. In addition, adverse reactions are often dose-dependent and vary between individuals. Gastrointestinal disorders Very common: Gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, mild gastrointestinal bleeding, which may lead to anemia in exceptional cases. Common: Dyspepsia, bloating, crampy abdominal pain, decreased appetite and gastrointestinal ulcers (with or without bleeding and perforation). Uncommon: Hematemesis, blood in the stool or bloody diarrhea. Rare: Intestinal stenosis. Very rare: Oral mucositis, glossitis, esophageal ulcers, constipation and lower abdominal discomfort, such as inflammation and bleeding of the large intestine, exacerbation of Crohn's disease/ulcerative colitis, pancreatitis. Cardiac disorders Very rare: Palpitations, water retention (edema), myocardial weakness (heart damage) and myocardial infarction. Blood and lymphatic system disorders Very rare: Hematopoietic disorders (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis) and hemolytic anemia. Nervous system disorders Common: Central nervous system disorders, such as headache, dizziness, drowsiness, anxiety, excitement or fatigue. Very rare: impaired sensitivity, impaired taste, memory impairment, disorientation, convulsions, tremors. Vision disorders Very rare: visual disturbances (blurred vision and diplopia). Ear and vestibular system disorders Very rare: tinnitus, temporary hearing loss. Renal and urinary system disorders Infrequent: increased edema, especially in patients with hypertension or renal impairment. Very rare: damage to renal tissue (interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), protein in the urine (proteinuria) and/or hematuria, nephrotic syndrome (water retention (edema) and proteinuria) associated with acute renal damage (renal failure). Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Infrequent: alopecia. Very rare: rash with redness of the skin (eczema, erythema, rash), photosensitivity reaction, skin petechiae, severe skin reactions, such as rash with blisters (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis/Lyell syndrome). Infections and infections Very rare: There have been reports of worsening inflammation (e.g. necrotizing fasciitis) due to infections during the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In addition, symptoms of non-infectious meningitis (aseptic meningitis) such as severe headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, stiff neck or confusion have been reported, and patients with autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease) seem to be at higher risk. Vascular disorders Very rare: high blood pressure. Immune system disorders Common: allergic reactions such as rash and itchy skin. Occasionally: urticaria. Very rare: severe systemic allergic reactions (manifested by swelling of the face, tongue and inner throat, with narrowing of the airways, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure and even anaphylactic shock), allergic inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis) and pneumonia. Hepatobiliary disorders Common: increased levels of liver enzymes in the blood. Occasionally: liver damage (especially in the case of long-term use), acute hepatitis (with or without jaundice). Very rare: fulminant hepatitis (which may have no symptoms beforehand). Mental illness is very rare: mental disorder, depression, anxiety, nightmare.
Contraindications:
Diclofenac sodium enteric-coated tablets: 1. Patients with known allergies to this product. 2. Patients who have asthma, urticaria or allergic reactions after taking aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. 3. Contraindicated for use during coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery.
Share:
Products
Our offers
Health Classification
Let us work together to protect precious health