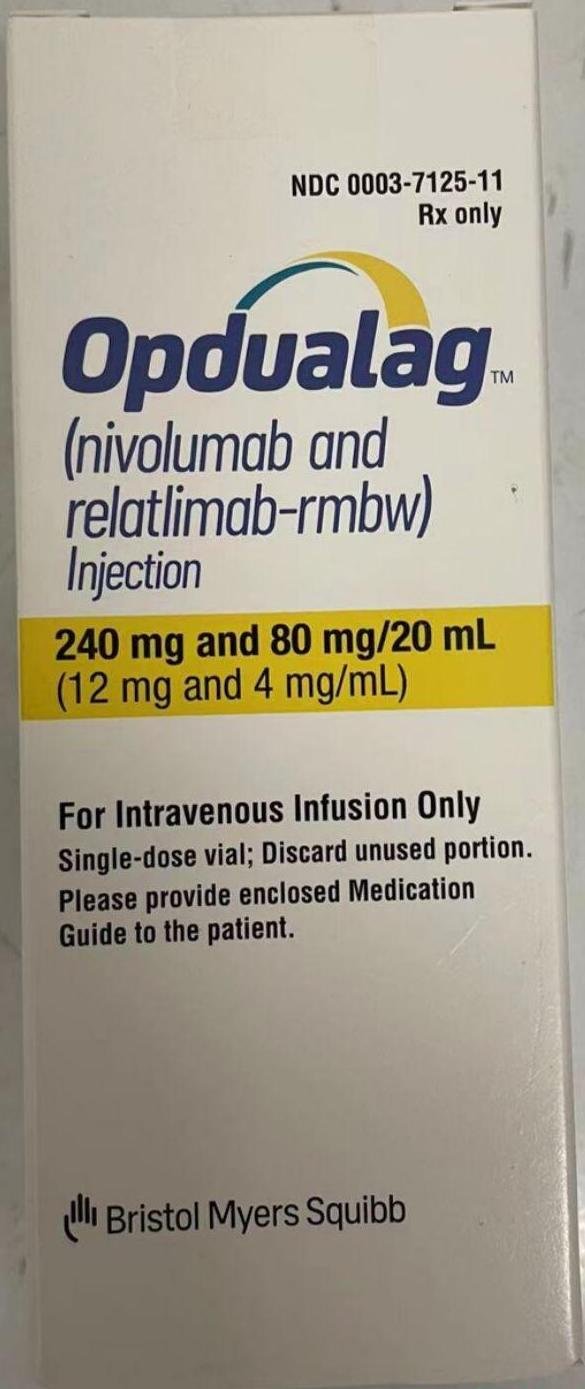
nivolumab and relatlimab Opdualag、奥普杜拉格
Indications
Opturag is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older weighing ≥40 kg with unresectable or metastatic melanoma.
Targets
LAG3xPD-1
Ingredients
Nivolumab, relaluzumab
Dosage Form
Injection
Specifications
20 ml vial/box
Indications
Indicated for patients aged 12 years and older weighing ≥40 kg with unresectable or metastatic melanoma. Children should be of sufficient weight to ensure pharmacokinetic stability.
Appearance
Colorless to pale yellow, clear solution.
Dosage and Administration
1. Recommended Dose
Adults and children weighing ≥40 kg: Administer opturag (nivolumab 480 mg + relaluzumab 160 mg) by intravenous infusion once every 4 weeks.
Infusion duration: Not less than 30 minutes.
2. Dose Adjustment
Opdulag is a fixed-dose combination. Individual dose adjustments of each component are not recommended. If specific adverse reactions occur, treatment delay or permanent discontinuation may be determined based on the severity of the toxicity. Severe immune-related adverse reactions require drug discontinuation.
3. Management of Infusion-Related Reactions
If an infusion-related reaction occurs, the infusion rate should be interrupted or reduced. In severe cases, the drug may be permanently discontinued, and supportive care should be administered.
4. Duration of Use
Treatment should continue until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurs. If the patient demonstrates clinical benefit and tolerates the drug well, treatment may be continued after radiographic progression.
Adverse Reactions
1. Common Adverse Reactions
Fatigue, rash, arthralgia, diarrhea, pruritus, musculoskeletal pain, etc.
2. Serious Adverse Reactions
Includes but is not limited to immune-related pneumonitis, hepatitis, colitis, and endocrine disorders (such as thyroid dysfunction, adrenal insufficiency, and type 1 diabetes).
3. Laboratory Abnormalities
Abnormalities in ALT, AST, creatinine, blood glucose, lymphocytes, hemoglobin, and electrolytes may be observed.
Precautions
1. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Reactions
Severe or even fatal immune-mediated events may occur, including pneumonitis, hepatitis, colitis, endocrinopathy, skin toxicity, nephritis, and myositis. Recommendations: Regularly monitor liver and kidney function, electrolytes, blood glucose, and thyroid function; administer glucocorticoids for moderate or severe toxicity; and discontinue the drug or permanently discontinue it if necessary.
2. Infusion-Related Reactions
If fever, chills, hypotension, or dyspnea occur, the infusion should be interrupted or discontinued, and supportive care should be administered.
3. Secondary Malignancies
There is a risk of developing secondary malignancies (e.g., squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, lymphoma) and should be evaluated regularly.
4. Evaluation of Continuation of Treatment After Disease Progression
If clinically stable and initial benefit is observed, continued treatment may be considered, but efficacy and safety should be closely monitored.
Use in Specific Populations
[Pregnant Women] There are no adequate human data. Animal studies have shown that rilalimumab can cause fetal toxicity, and its use during pregnancy should be avoided. Women of childbearing potential should use highly effective contraceptive methods and continue this method for at least 5 months after treatment.
[Lactating Women] It is unknown whether the drug is excreted in breast milk. Due to the potential risk, breastfeeding is recommended during treatment.
[Male and Female Patients of Reproductive Potential] Effective contraception is recommended during treatment and for 5 months after treatment. Direct data on reproductive effects are limited.
[Pediatric Use] This drug is approved for use in children 12 years and older weighing 40 kg or more. Safety and efficacy have not been established in children younger than this age.
[Elderly Use] No significant differences in efficacy and safety were observed in patients 65 years and older, but the risk of age-related diseases and complications should be considered.
[Renal Impairment] No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild to moderate renal impairment; data are limited for patients with severe renal impairment, so use with caution.
[Hepatic Impairment] No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild hepatic dysfunction; data are insufficient for patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment; monitoring of liver function and considering the risks are recommended.
Contraindications: Not specified in the labeling.
Drug Interactions
1. CYP Enzyme Interactions
The main ingredient of Opdulag is a monoclonal antibody that is not metabolized by hepatic enzymes and does not affect or significantly alter drug exposure through the CYP450 enzyme system.
2. Concomitant Use with Immunosuppressants
Avoid long-term concomitant use with systemic glucocorticoids or other immunosuppressants unless used to manage immune-related adverse reactions.
3. Interactions with Vaccines
Administration of live vaccines may increase the risk of infection; use of live vaccines should be avoided during treatment.
Share:
Products
Our offers
Health Classification
Let us work together to protect precious health